| 1 YEAR (Block C2) |
II semester | 6 CFU |
| (from Mechanics – Energetics) | |
| Prof. Marcello PUCCI |
A.Y. 2024-25 – program |
| Code: 80300151 SSD: ING-IND/32 |
LEARNING OUTCOMES:
The course aims to provide the students some theoretical instruments necessary for the comprehension and related application of the fundamentals of electric and hybrid electric propulsion systems, with particular emphasis to the on-wheel and ship propulsion.
The course will permit the students to acquire and apply the fundamentals of modelling and control of electric drives for the electric and hybrid electric on-wheel and ship propulsion, beside the supply and storage systems. The issues of the impact of electric vehicles on the power grid will also be discussed, with reference to modern vehicle-to-grid (V2G) and grid-to-vehicle (G2V) technologies.
KNOWLEDGE AND UNDERSTANDING:
In order to improve understanding of the topics, the implementation of drive trains simulation models will be addressed by using Simscape Electrical libraries in the Matlab-Simulink environment. The students will acquire the capability of comprehend and demonstrate the aware knowledge of the behavior of electric and hybrid electric vehicles, with particular reference to their electric propulsion, to the electric motors, power converters and related control systems- to the supply and storage systems. The understanding will be enhanced by the comparison between different types of electric drives, power electronic converters and
related control systems, as well as different types of storage systems. Several kinds of supplies and storage systems will be analyzed as well, with particular emphasis to the fuel
cells supplied vehicles.
APPLYING KNOWLEDGE AND UNDERSTANDING:
At the end of the course students will have to show the ability to independently apply the concepts learned with particular reference to the sizing of the drive train for electric and hybrid electric vehicles, power sources as well as the issues related to the interaction of energy storage on board of vehicles with the distribution network in terms of vehicle-to-grid (V2G) and grid-to-vehicle (G2V).
MAKING JUDGEMENTS:
Students will be able to collect and process independently specialized technical information on the design and control of electric drives as well as on energy storage systems used in electric and hybrid electric propulsion by road and sea and finally verify their validity.
COMMUNICATION SKILLS:
Students will be able to interact with specialists in power electronics and electric drives in order to elaborate the technical information necessary for the development of a design activity to be carried out individually or in groups.
LEARNING SKILLS:
The expertises acquired during the course will allow students to undertake higher-level training courses or apply for specialist technical roles in companies in the sector with a good degree of autonomy.
Prerequisities
It is suggested to have the basic knowledge of Electrical Network Analysis and Power Electronics
SYLLABUS
The course will be articulated in the following way:
– Electric Vehicles
– Hybrid Electric Vehicles
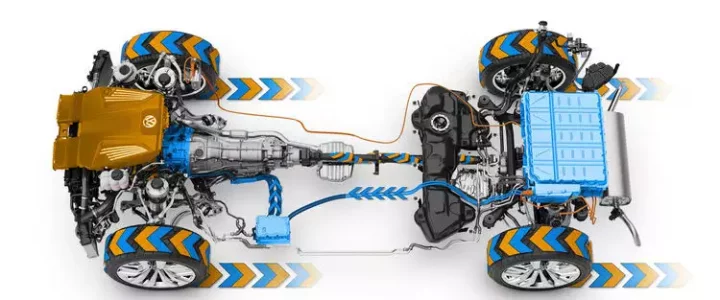
– Electric Propulsion Systems for vehicles
– Series Hybrid Electric Drive Train Design
– Parallel Hybrid Electric Drive Train Design
– Energy Storages (Batteries, Supercapacitors, – Ultrahigh-Speed Flywheels, Hybrid)
– Fuel Cell Vehicles
– Ship propulsion systems
– Vehicle to Grid (V2G) and Grid to Vehicle (G2V)
TEXTS
Educational material provided by the teacher
– John M. Miller, Propulsion Systems for Hybrid Vehicles, IET, 2008
– Iqbal Husain, Electric and Hybrid Vehicles: Design Fundamentals, 2010, CRC Press
– Mehrdad Ehsani, Yimin Gao, Ali Emadi, Modern Electric, Hybrid Electric, and Fuel Cell
Vehicles: Fundamentals, Theory, and Design, 2017, CRC Press
 UNIVERSITA' DEGLI STUDI ROMA "TOR VERGATA"
UNIVERSITA' DEGLI STUDI ROMA "TOR VERGATA"